Please select your location and preferred language where available.
Technology Topics
Introducing the latest technologies being researched and developed at KIOXIA Corporation and various use cases of flash memories.
-
We proposed a guideline for the reduction of parasitic resistance in channel-all-around TiO2 FeFETs based on in-depth electrical analysis. We revealed that the non-accumulated TiO2 channel is the main component for the parasitic resistance and demonstrated its 98% reduction by process optimization.
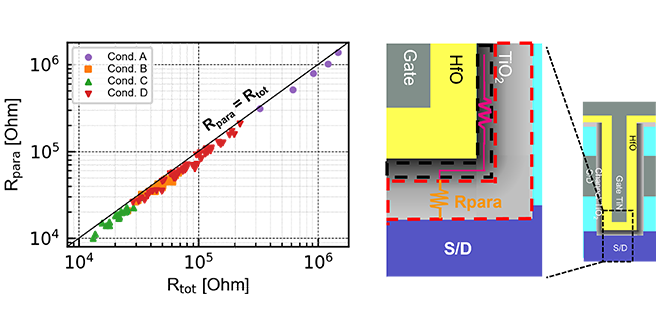
-
We theoretically investigated the behavior of domain walls (DWs) in nanotubes with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA). We formulated a model for spin-orbit torque-driven DW motion, enabling rapid quantitative prediction of DW shift characteristics. We presented important insights for device design, showing that DW velocity can be controlled by adjusting the nanotube diameter and magnetic properties.
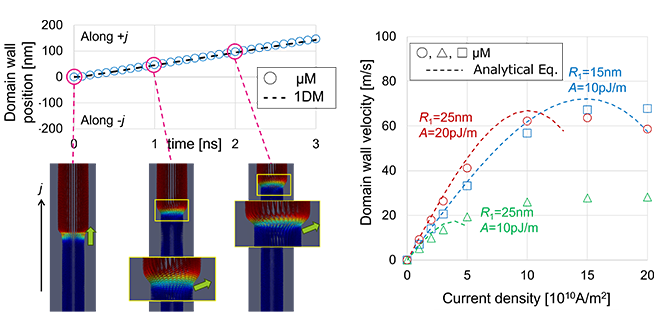
-
Spin-orbit torque magnetic random access memory (SOT-MRAM) is expected to be a new memory with high-speed operation and low power consumption. Conventional MRAM faced challenges with external magnetic fields disturbance, but as a solution, a ring-shaped magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) element with a closed magnetic circuit was proposed. The micro-magnetic simulation demonstrated that the storage layer of the Ring-shaped MTJ exhibits a stable coherent magnetization reversal.
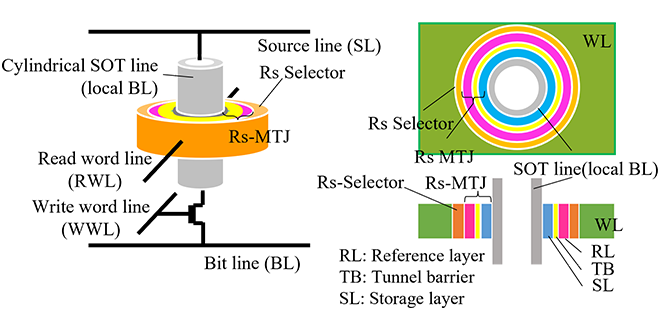
-
We demonstrated a highly reliable vertical gate-all-around transistor with an oxide-semiconductor channel in a scaled dimension by process and structural optimization. This achievement proves that the oxide-semiconductor transistor technology is promising for future new memory application.
-
We fabricated a 64 Gbit cross-point MRAM (Magnetic Random Access Memory) with the world’s smallest cell area of 0.001681 μm2 and demonstrated reliable memory cell operation. This achievement paves the way for MRAM applications in SCM (Storage-Class Memory).
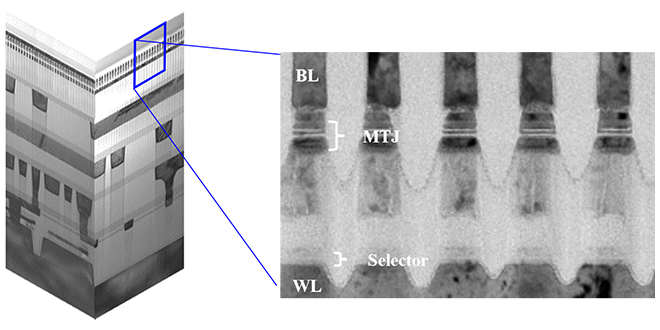
-
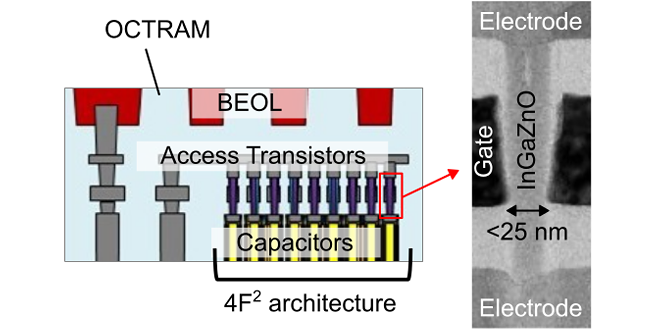
Kioxia, in collaboration with Nanya, developed Oxide-semiconductor Channel Transistor DRAM (OCTRAM) technology. The ultra-low leakage properties of InGaZnO transistors enabled long data retention over 100 sec, providing significant advantages in power saving compared to conventional DRAM.
-
We are developing magnetic domain wall memory as one of the candidates for a new file memory. We have proposed and demonstrated a novel stable writing scheme where writing is performed by the current-induced magnetic field. By gradually stopping the write current pulse, the device is cooled while applying current magnetic field, achieving the stable writing with low error rate. These results were presented in SSDM 2024.
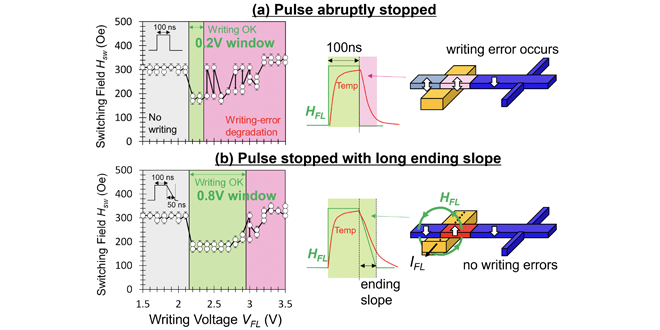
-
Rapid advances in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are increasing the demand for non-volatile emerging memories with high speed operation. We have demonstrated, for the first time, memory operation of Channel-All-Around FeFET, and realized high ΔIon>2μA and stable endurance (>106cycle) in the smallest footprint ever (707nm2).
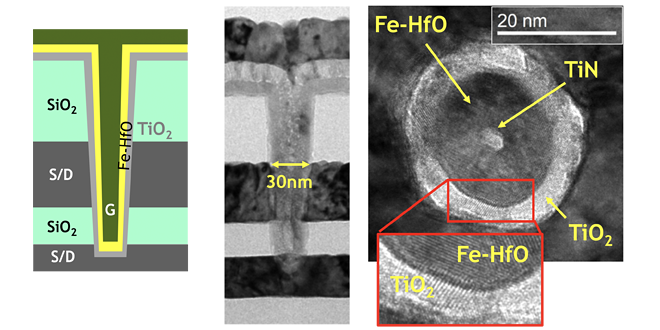
-
We have investigated the stress-time dependent degradation of magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) in high-density spin-transfer torque magnetic random access memory (STT-MRAM). We have proposed mechanism and suppression methods of the degradation using the density functional theory calculation and time-evolution model. Our findings provide valuable insights into the reliability in high-density STT-MRAM. This achievement was presented at the IRPS 2024.
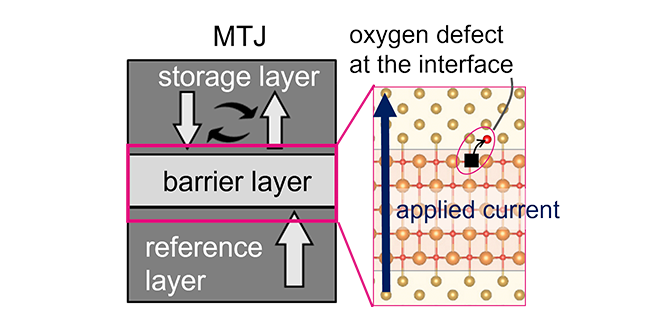
-
The limited endurance is one of the major challenges in Si channel FeFET, which has attracted much attention as candidates for next-generation memory. By combining trap-controlled interfacial layer (TCIL) and the charge-control operation sequence, MW of >2 V in FeFET has been achieved even after 107 cycles.
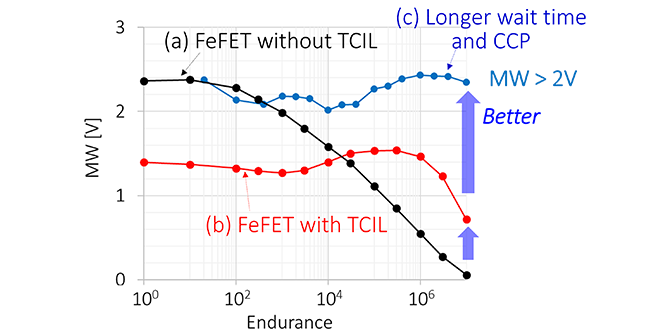
-
We have demonstrated a novel 14nm magnetic tunnel junction(MTJ) for achieving high-retention and high-speed writing simultaneously in 1Z (15-14) nm Spin-Transfer-Torque(STT) MRAM. Our MTJ, called as AccelHR-MTJ(Accelerated STT-Switching and High-Retention MTJ), can show excellent performances such as high-retention of >10 years at 90℃ and high-speed writing down to 5ns. This achievement was presented at the IEDM 2023.
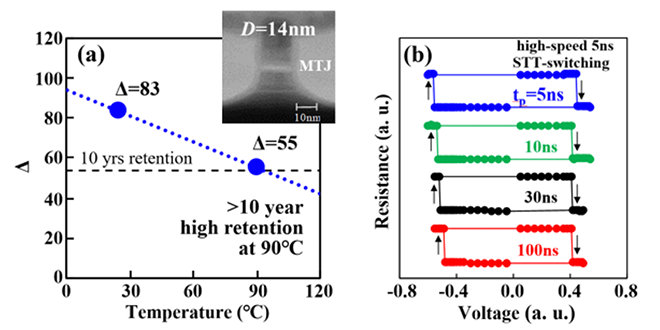
-
Spin orbit torque(SOT) driven magnetization switching has recently attracted attention towards next generation magnetic memory. In this report, we newly introduced a canted bias magnetic field and clarified that it makes the SOT driven perpendicular magnetization switching faster and more stable. This was presented at International Conference on Solid State Devices and Materials in 2023(SSDM2023).
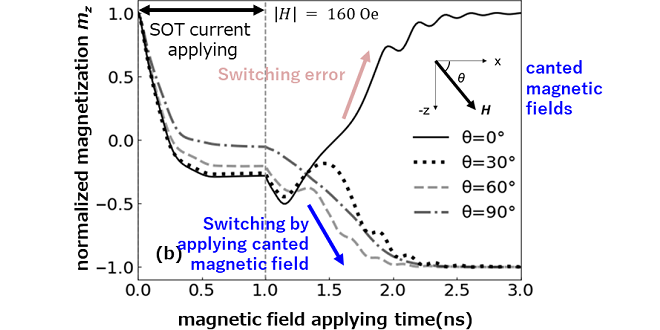
-
We demonstrated a multi-level phase change memory (PCM)/Selector cell which can be programmed without iterative verify operation. Optimal thermal and composition design enabled to form distinct middle resistance state, in which crystalline and amorphous co-exist at designed positions. Multi-level programming was achieved by one single pulse, and it was stable over 107 cycles, making it promising for future cost-effective, large-capacity, and high-speed cross-point memory.
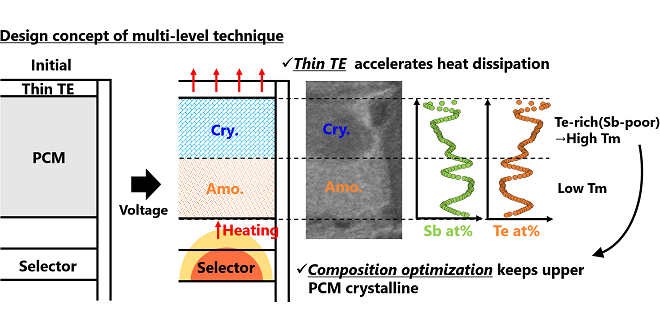
-
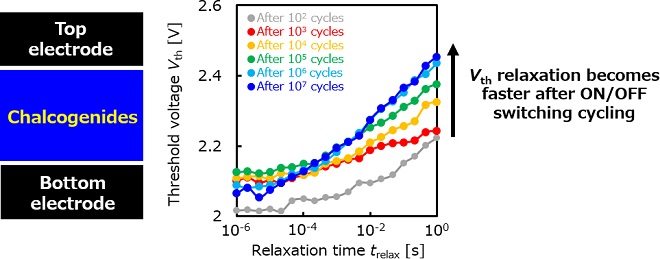
HfO2-based Ferroelectric Field-Effect Transistor (FeFET) is a promising candidate for next-generation memory. This study clarified that program/erase cycling generated new trap sites in interfacial SiO2 layer disappears with time. This recovery phenomenon has a non-negligible impact on the threshold voltage behavior during retention process. These results were presented at the international conference SSDM 2023.
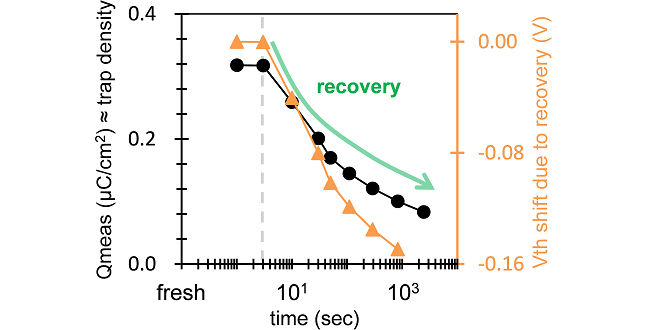
-
Imprint* is one of the critical reliability challenges in HfO2-FeFET, which has attracted attention as candidates for emerging high-speed memory devices. We have clarified the relationship between spontaneous polarization, trap charge, and imprint by charge component analysis. This result was presented at the international conference SSDM2023.
* Phenomenon in which the voltage required for polarization reversal(coercive voltage Vc) in a ferroelectric film shifts while the polarization state is maintained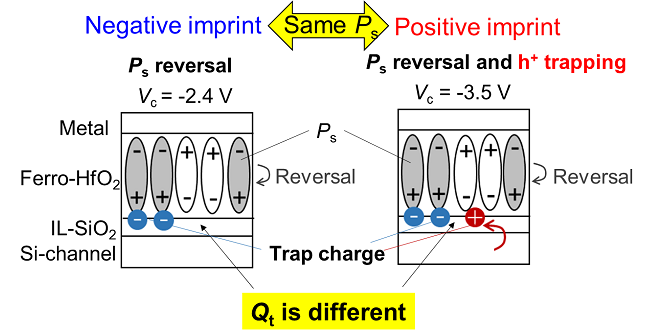
-
We developed a recovery annealing technology applicable to 7-bit per cell flash memory operating at cryogenic temperatures. The technology can contribute to the realization of a sustainable society through future bit cost scaling and extended chip life.
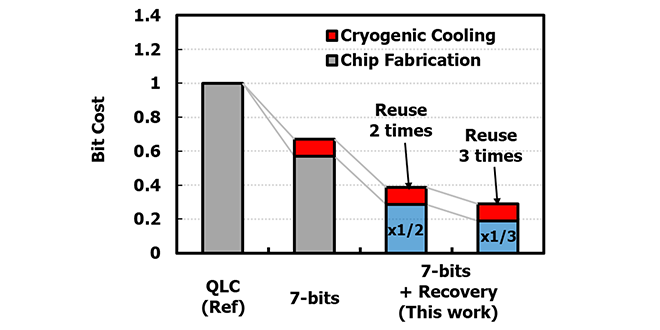
-
We have successfully demonstrated the preparation of ferromagnetic Co thin layers showing the current-induced domain wall motion (CIDWM), by using atomic layer deposition technique which is widely utilized in the three-dimensional LSI technologies. CIDWM is the key physical phenomenon for race-track memory[1]. This result was presented in the international conference, IEEE INTERMAG 2023[2].
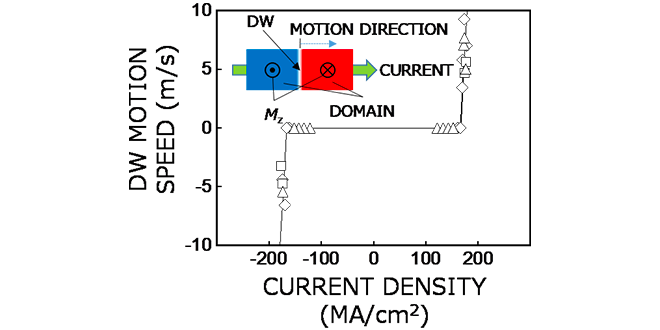
-
We developed new analysis method which can evaluate trap characteristics in short time domain. And we clarified whole picture of hole trapping in SiN film which is essential to improve charge trap memory devices. These results were presented at the international conference IRPS 2023.
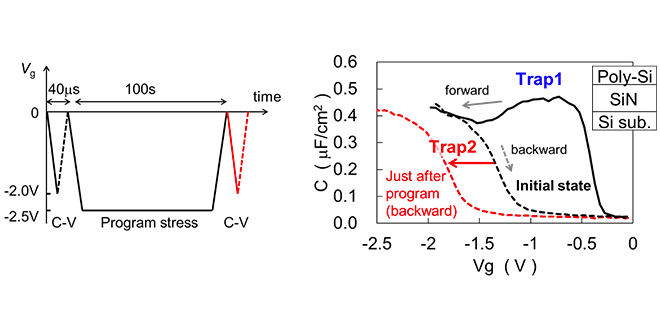
-
HfO2-based FeFET is a promising candidate for next-generation memory. The coupling between polarization reversal and charge trapping was revealed in this study. We demonstrated a novel operation scheme that strongly suppresses unintended programing of FeFET during memory array operation. These results were presented at the international conference IRPS 2023.
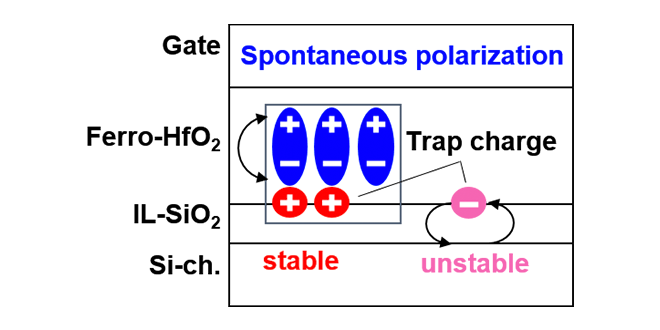
-
Ferroelectric MOS transistors using HfO2 as the dielectric and Si as the current path have been widely researched and developed for memory applications including AI applications. Kioxia has fabricated a prototype ferroelectric Field Effect Transistor (FET) using TiO2 as the current path and demonstrated high-speed, low-voltage operation and high cycle endurance. This achievement received the Best Contributed Paper Award at the international conference EDTM2023.
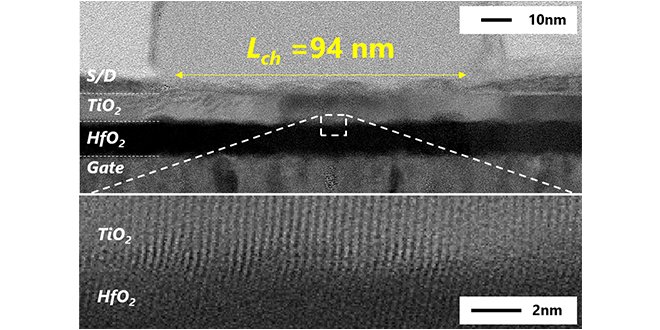
-
Selector devices are key components for next-generation high-density memory cell arrays. In this work, the reliability of selector devices has been studied in collaboration with imec, the world-leading R&D center in electronics technologies. The mechanism of the cycling-dependent threshold voltage instability has been clarified by combining electrical characterization and modeling techniques. These results were presented at the international conference IEDM2022.
-
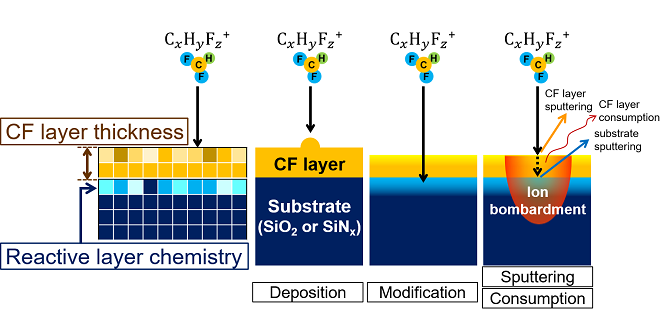
As the demand for larger memory capacities has rapidly increased, a high etch rate for a high aspect ratio structure is significantly required for high productivity. We have modeled ion-induce surface reactions and developed a simulation technique for predicting the optimal ion species for the etching process of the memory hole because ion species play a dominant role in high aspect ratio etching.
-
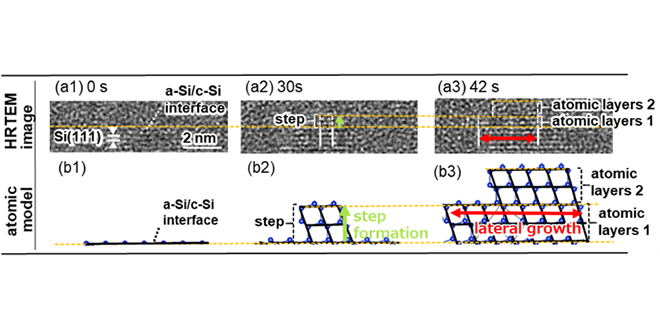
In 3D LSI, transistors are formed on polysilicon. The formation of defect-free polysilicon is important for high performance transistors. To establish the formation process, we improved the conventional electron microscope technology and observed the growth process of crystal grains on an atomic scale in real time.
-
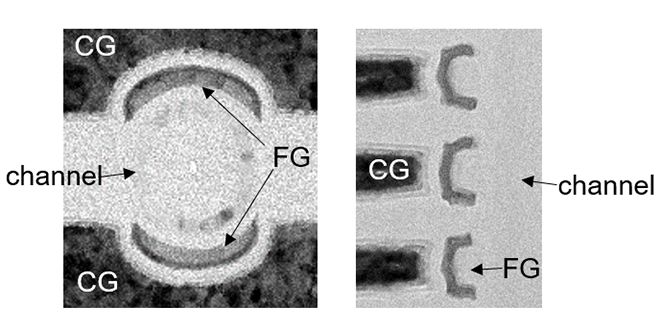
Large program/erase window, tight Vth distributions and superior data retention characteristics, which were essential to achieve multiple bits per cell, realized by optimizing read operation and FG structures in split-gate cells.
-
We successfully demonstrated the world’s first 7-bit per cell by combining 77K cryogenic operation with silicon process technology that can improve memory cell characteristics.
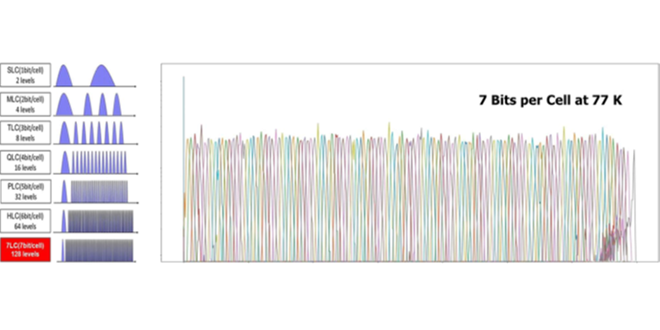
-
HfO2-FeFETs is a strong candidate for next-generation memory. In HfO2-FeFETs memory the difference between "0" and "1" decreases after repeated write and erase operations. This cycle degradation, which remained largely unknown, has been clarified by high-speed charge center analysis. This achievement is expected to advance the practical application of HfO2-FeFET memory. These results were presented at the international conference IEDM2021.
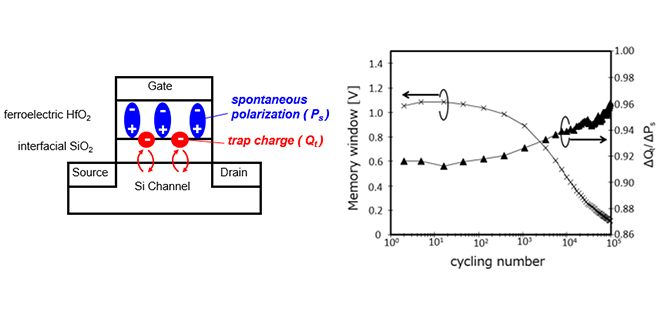
-
With the growth of the quantum computing and high performance computing, there are increasing demands for the computer systems and electrical components that can operate at relatively low temperature. It has been reported that the characteristics of several types of semiconductor devices can be improved by cryogenic temperature. This report is the first to introduce a cryogenic operation and characteristics of 3D Flash memory at 77 K immerged in the liquid nitrogen.
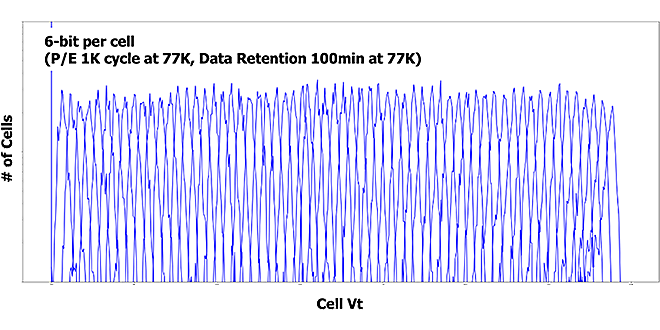
-
OS-FET with both high thermal stability and high on-current can be realized by optimizing F amount in IGZO:F. These results are fundamental technologies to realize new memory devices with large amounts of storage, low latency, and ultralow-power consumption, which cannot be achieved by silicon-based FETs.
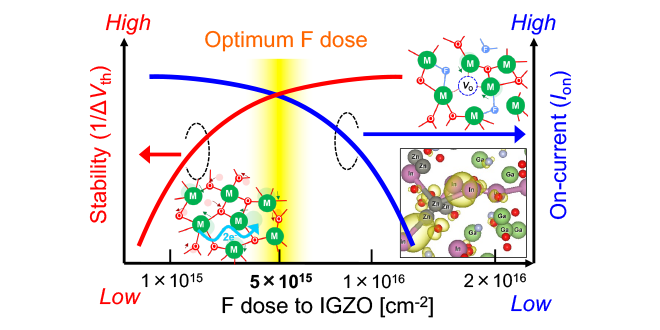
-
Recently, ferroelectric memories using ferroelectric-HfO2 film have attracted much attention towards low-power and high-density in-memory computing for AI (artificial intelligence).
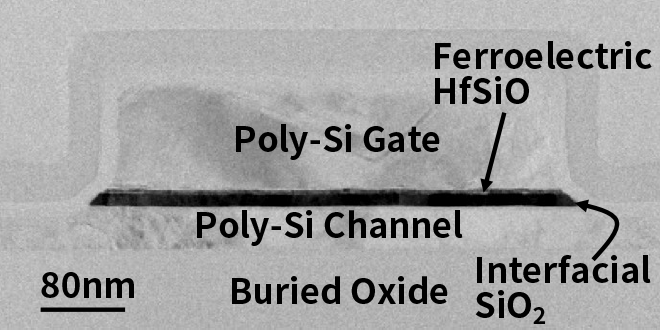
-
BiCS FLASH™ can increase its memory density and reduce the product cost by increasing the number of word line (WL) layers. The thyristor structure is one of the promising candidates to obtain a large read current even the number of stacked layers is increased.
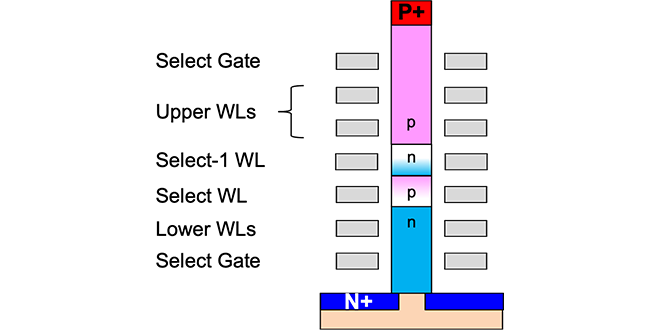
-
A challenge of OS-transistor development is improvement of its thermal stability. By using InGaZnO (IGZO) which is a conventional OS, the OS transistor does not work properly by thermal processes required in manufacturing process of the memory device.
In order to overcome this issue, we have newly proposed InAlZnO (IAZO) as an OS material with high thermal stability.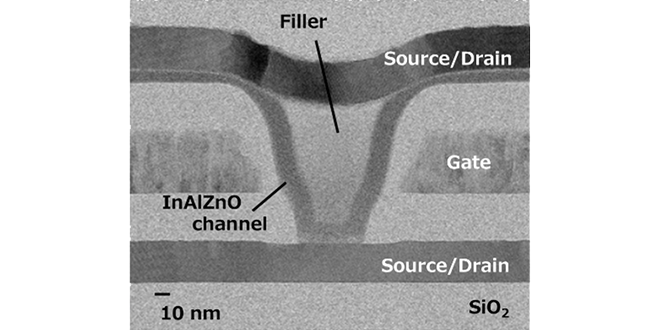
-
By applying MILC(Metal-induced Lateral Crystallization) technology to Si film in the vertical memory holes, we successfully fabricated the formation of monocrystalline Si from amorphous Si via nickel silicide.
The 3D flash memory cell devices equipped with this technology demonstrated superior electrical characteristics and reduced variation compared to conventional devices using poly-Si as the channel.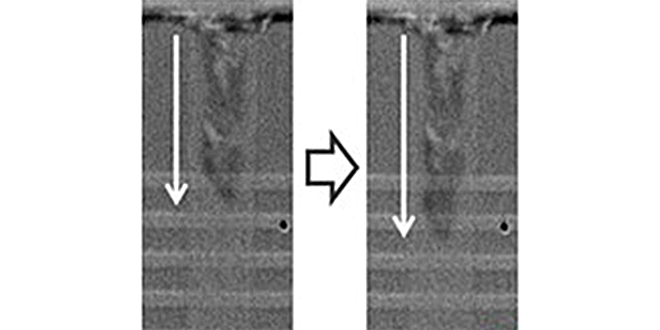
-
Three-dimensional (3D) semicircular split-gate flash memory cells have been successfully developed for the first time.
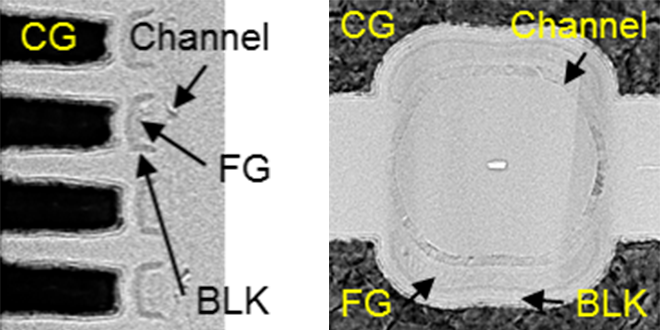
-
The challenge for achieving terabit-scale cross-point memory is to reduce operation current of a memory cell.
As a solution, we focused on a new non-volatile memory; Ag ionic memory.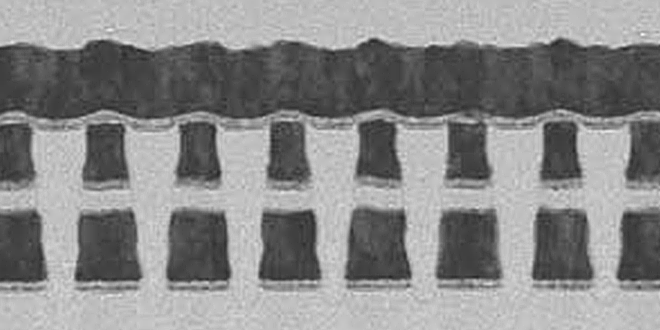
-
We have established a brand-new evaluation method for nanomaterials by applying the state-of-the-art semiconductor fabrication process.
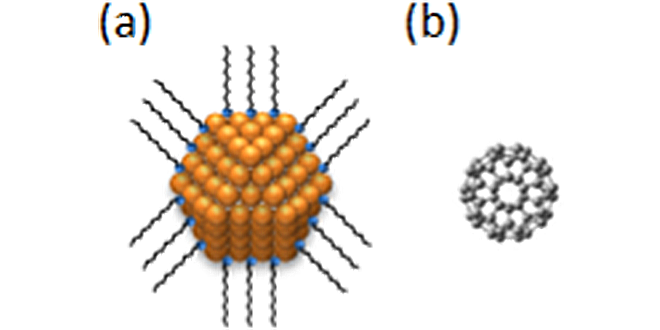
-
Memory devices that require new materials and complex 3D structures.
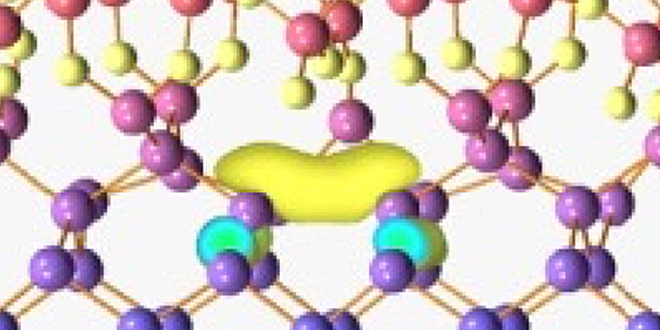
-
We propose new memory cell technologies to realize even higher bit density file memories, as well as various high-speed nonvolatile memories.
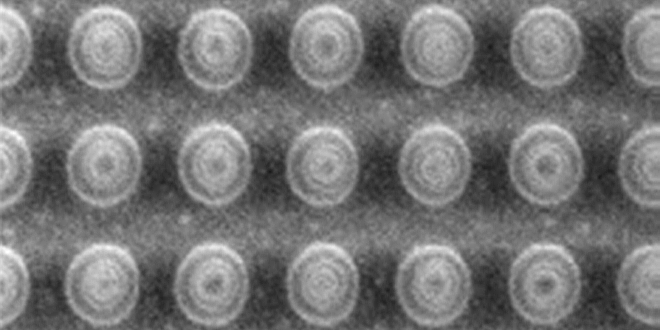
R&D Organization
We aim to pursue continuous technological exploration and its social implementation to achieve an affluent and sustainable digitalized society through innovative memory technologies.
Conducts R&D on BiCS FLASH™, a type of 3D flash memory that KIOXIA was the first to develop in the world, while serving as a bridge between R&D and volume production.


