Please select your location and preferred language where available.
Reduction of parasitic resistance in channel-all-around TiO2 FeFETs for high speed non-volatile memory application
December 23, 2025
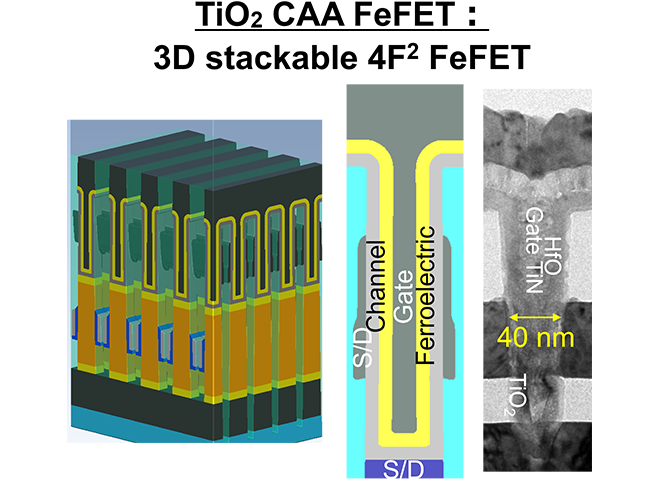
A 4F2 ferroelectric memory device with TiO2 channel; vertical TiO2 Channel-All-Around (CAA) FeFET has a performance and scalability suitable for high-density and high-speed memory Figure 1[1]. Further device scaling needs an improved drive current because the device scaling with smaller contact area could degrade the drive current which is essential for high-speed application. In this study, therefore, we conducted an in-depth electrical analysis on the parasitic resistance in the vertical TiO2 CAA FeFET and discussed its mechanism.
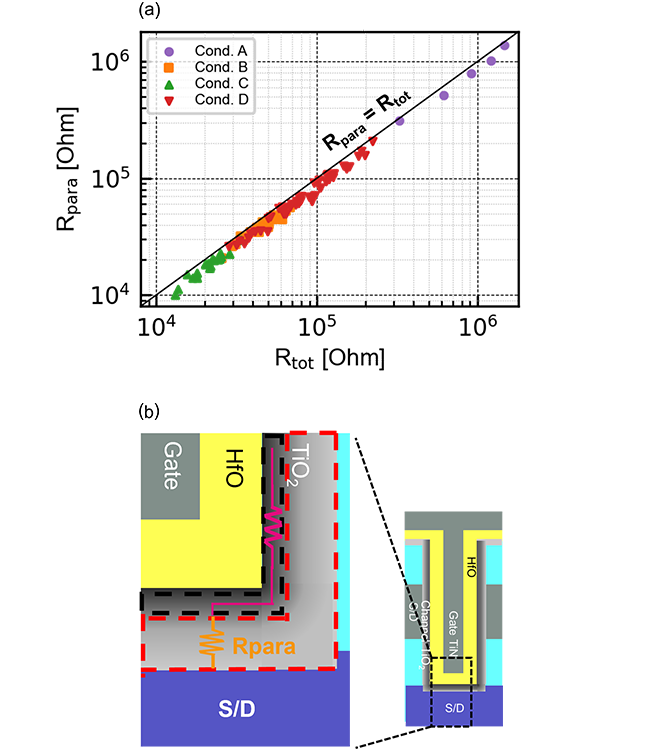
Figure 2(a) shows parasitic resistance (Rpara) in the TiO2 CAA FeFET as a function of its total resistance (Rtot). It is found that the Rpara accounts for around 85% of the Rtot irrespective of device structure and fabrication process. This result implies that the mechanism of Rpara in the TiO2 CAA FeFET is different from that in conventional FETs, and we proposed a novel parasitic resistance model, where the non-accumulated TiO2 channel dominates the Rpara Figure 2(b).
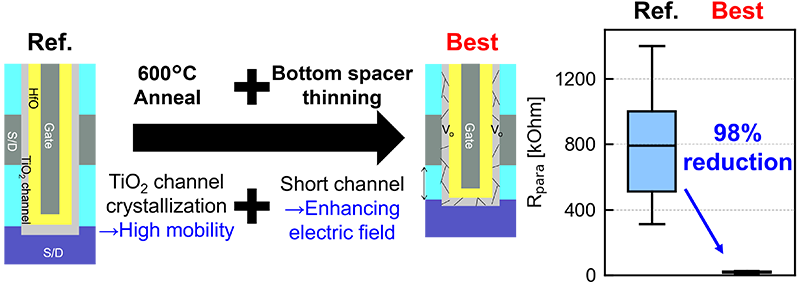
The proposed model indicates that channel engineering is key for Rpara reduction, rather than contact engineering. We conducted process optimizations that enhance carrier density and mobility in the TiO2 channel, as well as structural optimizations that increase electric field across the non-accumulated channel region. As a result, we demonstrated 98% reduction in the Rpara with the optimized device structure Figure 3.
The model and design guideline proposed and demonstrated in this study can help further performance improvement of CAA transistors aiming for high-speed memory application.
©2025 JSAP

©2025 JSAP

©2025 JSAP
This achievement was presented at the 2025 International Conference on Solid State Devices and Materials.
Reference
[1] S. Kabuyanagi et. al., “A Vertical Channel-All-Around FeFET with Thermally Stable Oxide Semiconductor Achieving High ΔIon > 2μA/cell for 3D Stackable 4F2 High Speed Memory”, 2024 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology and Circuits, T8-2.
[2] K. Kawaguchi et. al., “Mechanism and Mitigation of Parasitic Resistance in Vertical TiO2 Channel-All-Around FeFET towards High-Speed Memory Application”, 2025 International Conference on Solid State Devices and Materials.

