Please select your location and preferred language where available.
Coherent Spin-Orbit Torque Magnetization Switching of Ring-shaped MTJ for High-density SOT-MRAM
December 9, 2025
Spin-orbit torque (SOT) magnetization switching is most promising as next-generation technology for future magnetic random-access memory (MRAM). It offers advantages such as high-speed writing, low power consumption and high endurance. However, magnetic stability and immunity are critical factors in conventional MRAM that uses dotted magnetic tunneling junctions (MTJs), especially for achieving high density.
To address them, we propose a new magnetically stable cell architecture with a ring-shaped magnetic tunneling junction (Rs-MTJ) as illustrated in Figure 1. The SOT-MRAM cell basically consists of an Rs-MTJ, an Rs-selector, a write transistor and a vertical SOT line with a cylindrical structure. Owing to the formation of a closed magnetic circuit within the Rs-MTJ, it is expected to enhance magnetic stability in the static storage state and improve magnetic immunity.
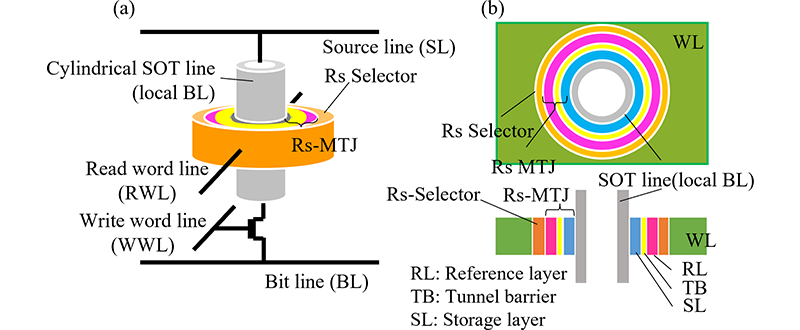
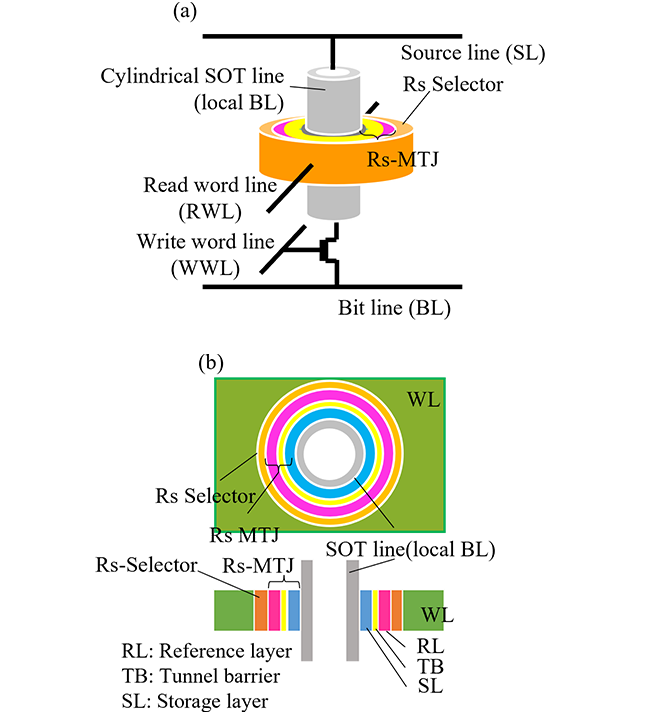
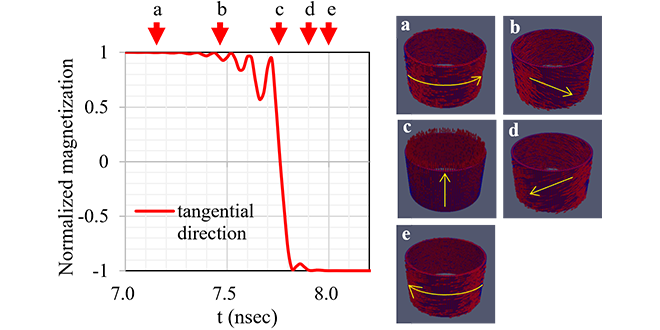
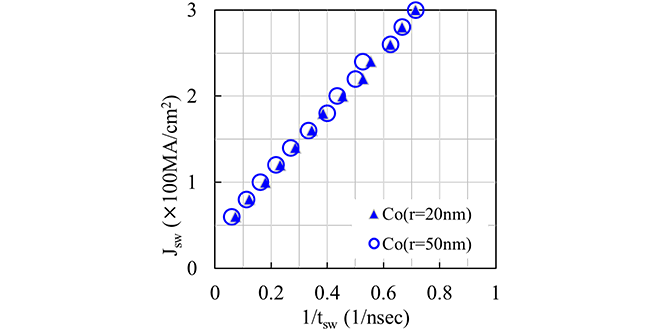
The SOT switching behavior in the Rs-MTJ has not been thoroughly explored so far. To clarify this, we investigate it using the micro-magnetic simulation. Our analysis of the SOT switching of the ring-shaped storage layer (Rs-SL) reveals stable coherent SOT magnetization reversal utilizing the practical MTJ material, such as cobalt, seen in Figure 2. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the SOT switching current density (Jsw) is inversely proportional to the SOT switching time (tsw) as shown in Figure 3. It indicates that the SOT switching behavior of the Rs-MTJ is described by the macro-spin model.
We also estimate the magnetic retention energy (ΔE) and the current density (Jc) at the SOT writing operation through the analytical calculation based on the macro-spin model. The results indicate that these can be optimized for scalability by adjusting the radius (R), the height (L) and the thickness (t) of the Rs-SL.
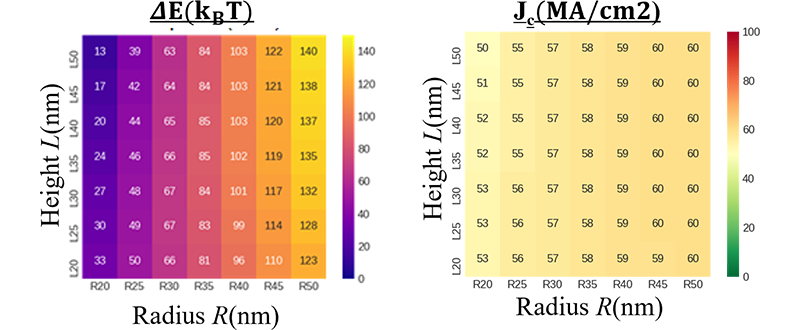
This achievement was presented at the 2025 Joint MMM-Intermag conference.
Reference
[1] M. Yoshikawa et al., 2025 Joint MMM-Intermag Conference, FR-05, New Orleans, LA, USA (2025).

