Please select your location and preferred language where available.
Optical SSDs: Enabling Next-Generation Green Data Centers


April 24, 2025
Today, information plays a vital role in both personal and business contexts. For companies, it is a critical asset that directly influences their success and longevity. Most information is stored as data on SSDs or other storage devices, either in data centers or on-premise servers. While sending, receiving, and storing data is predominantly handled by electrical connections, there is a growing movement to adopt optical connections as a new option. Kioxia is advancing optical technology with focused research and development of Broadband Optical SSDs.
Modern Conveniences are Driving Increased Data and Power Consumption
Advancements in AI and digital technology have made everyday life noticeably more convenient and interconnected. Technology we use daily—like computers, smartphones, and home appliances—is becoming more powerful, while access to various online services continues to grow. The rise of generative AI has also introduced new services, such as translation, document summarization and planning, further enhancing convenience.
Once we experience these benefits, it’s hard to imagine life without them. A robust power infrastructure that supports large-scale, high-performance data centers is essential to maintaining and improving our quality of life in the digital world while protecting the planet for future generations.
As data centers grow in number and complexity, the devices operating within them are becoming faster and more powerful. High-bandwidth, low-latency networks are also expanding to keep up with rising demand. Relying solely on existing technologies could lead to disruptions—such as sudden data center outages—could interrupt electronic payments for online shopping, video streaming services, telemedicine, and even government and corporate systems.
To keep pace with technological progress while minimizing environmental impact, developing sustainable solutions that enhance both performance and energy efficiency in data centers is essential. A balanced approach that considers environmental, social, and economic factors will be key to supporting future growth responsibly.
Learn more about the basics of data center and storage
An easy-to-understand explanation via Doujinshi (Manga).

Optical Technology: Transforming Data Centers from Within
Currently, the major components in the servers running in data centers, including CPUs, SSDs and NICs, are connected via PCI Express® (PCIe®). PCIe is a connectivity standard that enables high-speed data transfers between devices and the CPU and has doubled in bandwidth with each new generation. Widening the frequency range used for data transmission creates higher bandwidth, enabling high-speed communication and high-capacity data transfers.
For example, PCIe 4.0 transfers data at 16 giga transfers (GT/s), while PCIe 5.0 transfers data at 32 GT/s*1.
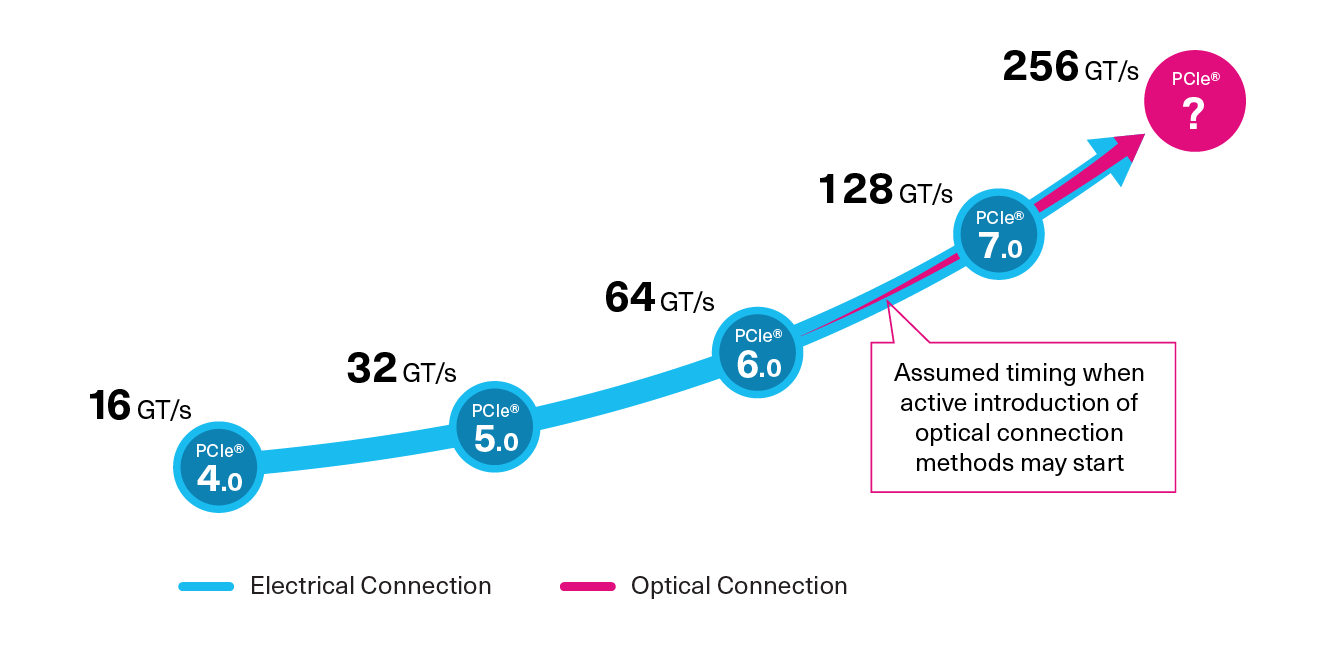
- Transfer rates are measured in giga transfers and represent the theoretical maximum speed before encoding; actual speeds may be slower.
- As of August, 2024. Kioxia Survey.
PCI-SIG is currently evaluating the next-generation (PCIe 7.0), and steps are being taken to incorporate optical connectivity in addition to traditional electrical connections as a standard.
There are numerous advantages to enhancing data center flexibility, optimizing system configurations, and streamlining operations.
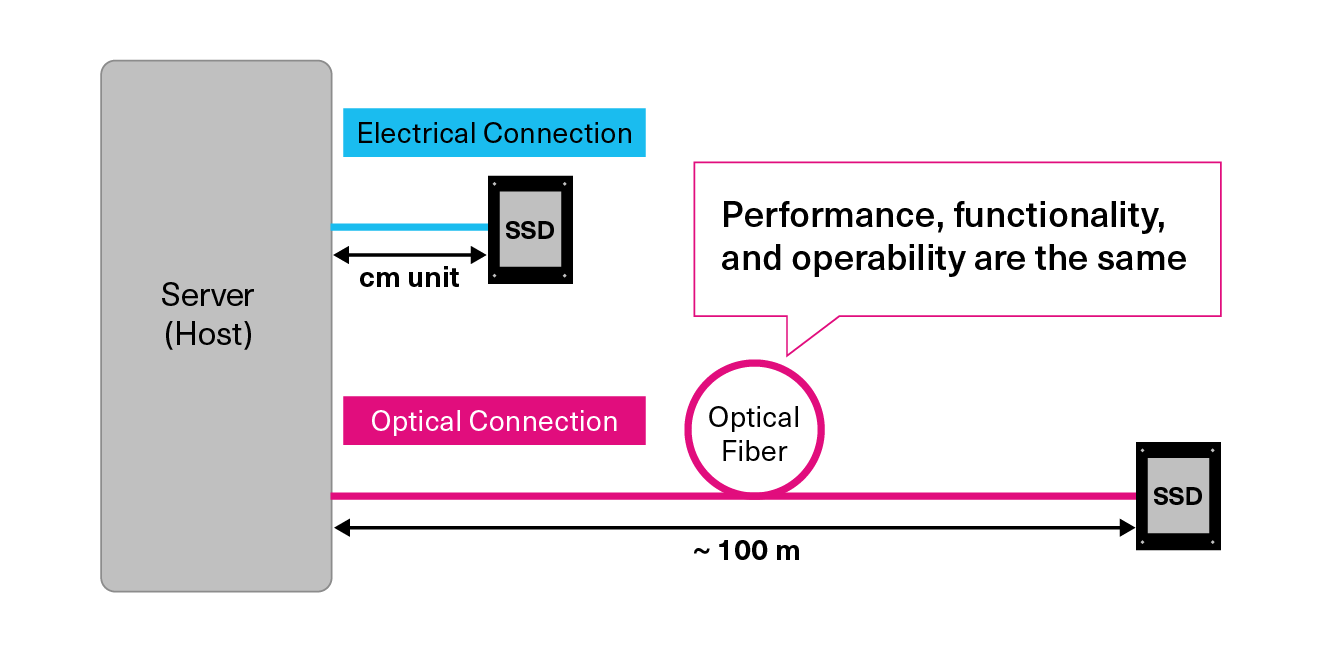
Optical Advantage 1: Dynamic Extension of Distance Between Server and SSD
For example, optical connections can dramatically extend the physical distance between key components, such as the server (host) and SSDs. This flexibility in component placement, which was previously restricted to a single chassis, can contribute to more efficient data center design, operation, and maintenance.
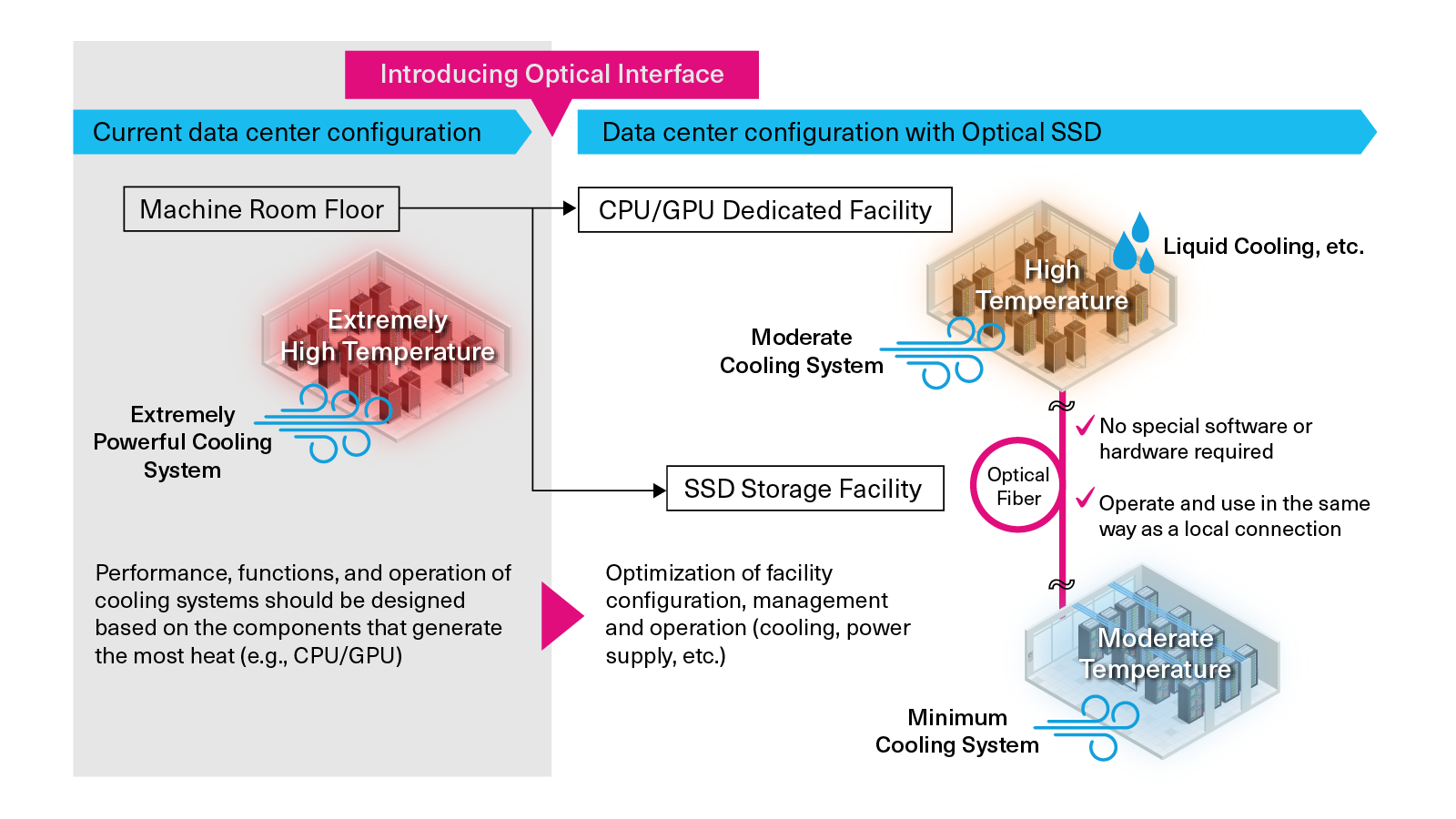
Optical Advantage 2: Addressing Heat Generation Issues
To handle larger data volumes at higher speeds, data centers require a substantial number of high-performance servers. This increases power consumption and heat generation, leading to higher temperatures and the risk of server malfunctions and system downtime due to power interruption. Many current data centers are designed to cool servers based on the highest heat-generating components, often resulting in energy waste from overcooling lower-power components.
By using optical connections to extend server components and arranging them according to heat generation, cooling systems—such as liquid and air cooling—can be optimized, preventing overcooling and improving overall efficiency.
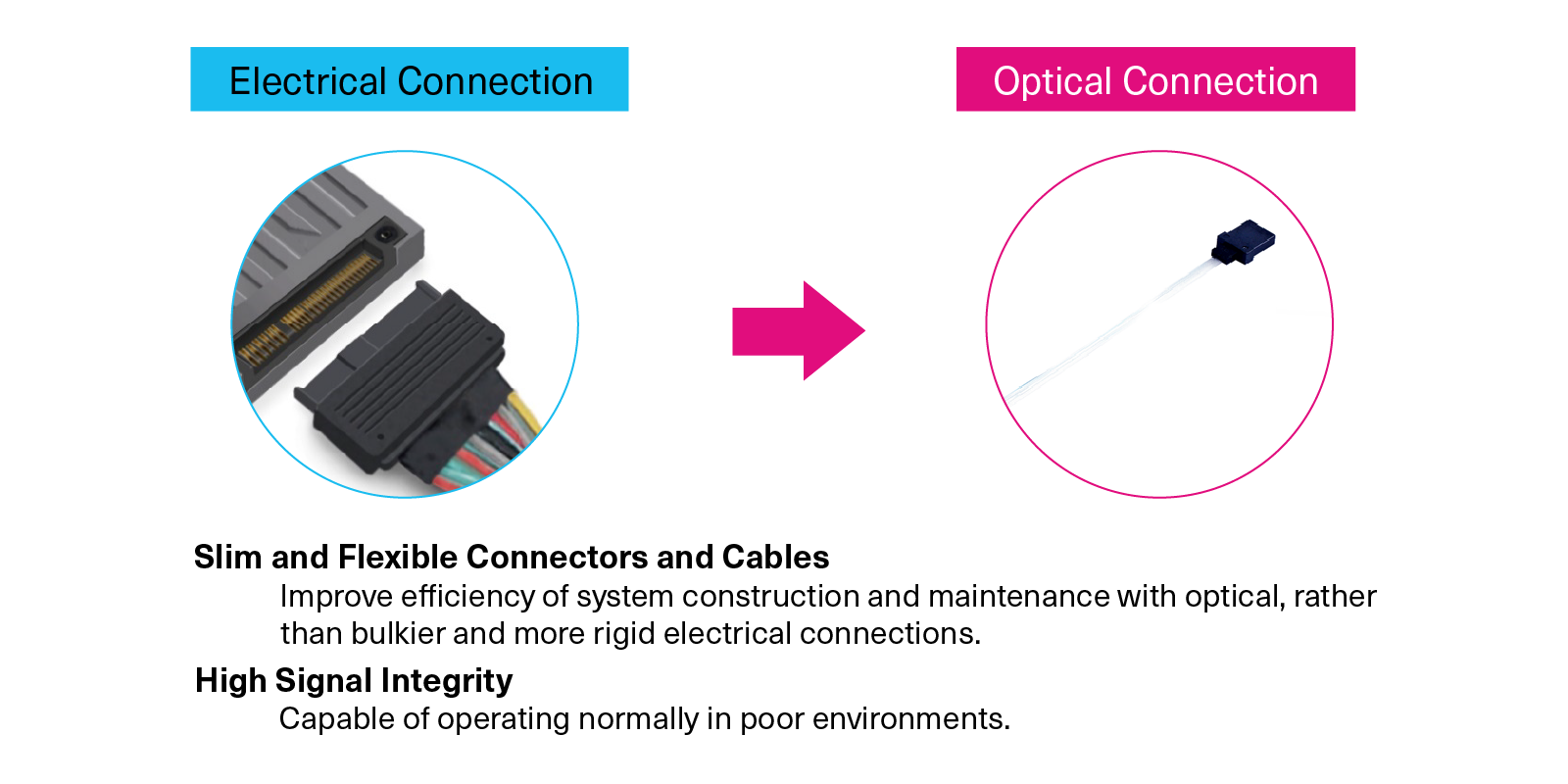
Optical Advantage 3: Slim, Flexible Cables and Connectors
Optical cables offer the same bandwidth as electrical cables but feature slimmer, more flexible connectors and cables, making system construction and maintenance easier and more efficient than with bulkier, harder electrical cables (harnesses). Additionally, eliminating signal noise (which occurs in electrical cables) allows for operation in challenging environments, such as in space or in factories.
Next-Generation Green Data Center Technology Development Project: Collaborating to Address Explosive Data Growth
The Next Generation Green Data Center Technology Development Project is a Japanese national effort that was publicly solicited by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) in February 2022. Kioxia has been selected for this project, along with Fujitsu Limited, NEC Corporation (NEC), AIO Core Co., Ltd., Furukawa FITEL Optical Components Co., Ltd., and KYOCERA Corporation.
These companies are working together to drive technological advancements in data centers that address the rapid growth in data volume, with a focus on improving energy efficiency, increasing capacity, and reducing latency. The project goal is to match the performance and processing capacity of current data centers while using 40% less energy by 2030.
Research and Development Addressed by the Japan National Project
- Optoelectronics technology (development of photoelectric fusion devices and optical smart NICs)
- High-performance and energy-saving technologies for optics-compatible chips, etc. (development of power-saving CPUs, power-saving accelerators, and Broadband SSDs)
- Disaggregation technology
* Table can be scrolled horizontally.
|
AIO Core Co., Ltd. |
Fujitsu Limited |
Furukawa FITEL Optical Components Co., Ltd. |
KYOCERA Corporation |
Fujitsu Limited |
NEC Corporation |
KIOXIA Corporation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Photoelectric fusion device |
CPO application technology |
High modulation efficiency optical engine technology |
Optoelectronic device package technology |
Energy-saving CPU |
Disaggregation technology |
Optical SSD |
In next-generation green data centers, by adopting optical technology in system design, components like SSDs and CPUs can be disaggregated and flexibly interconnected. This approach improves installation flexibility, enhances data processing, and enables dynamic system configurations optimized for specific applications, further advancing disaggregated computing systems. The result is greater data center efficiency, real-time resource management and data analysis, and a more sustainable IT infrastructure.
What is a Disaggregated System?
A disaggregated system is an architecture implementing optically connected systems, designed to enable flexible separation and optimization of computing resources. The use of optical technology supports high-speed data processing and access based on highly flexible system design, offering both better performance and environmental benefits.
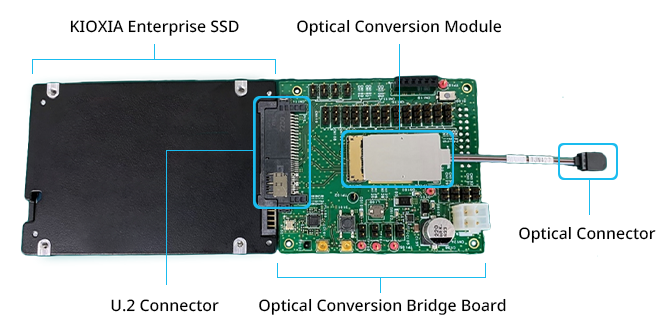
KIOXIA Broadband Optical SSD
As part of the project, Kioxia is responsible for the research and development of broadband optical SSDs, which includes the following three innovations:
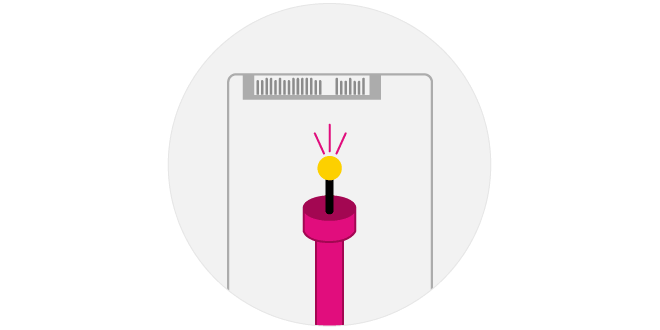
Optical SSD
Realization of an optical interface SSD by developing a photoelectric conversion bridge board, designed to connect with Kioxia's business-oriented SSDs.
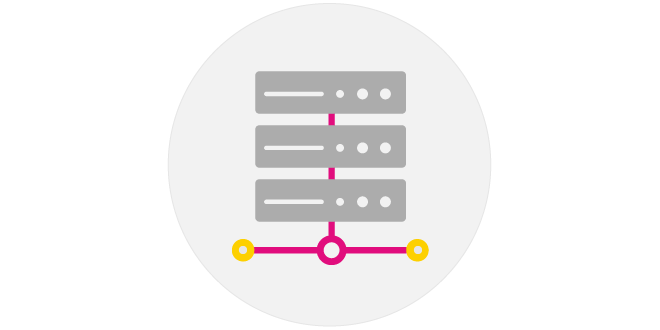
Storage System
Development of hardware designed to aggregate and store multiple optical SSDs, equipped with functionality to support external control.
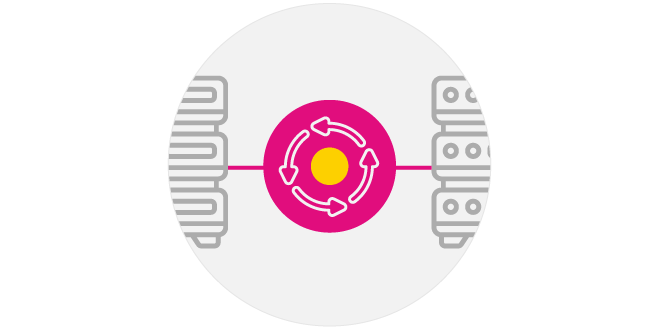
Storage Management Software
Development of software that utilizes disaggregation technology for efficient system operations, in collaboration with SSDs, as part of research and development activities at NEC Corporation.
Kioxia presented the optical SSD concept to the public for the first time at FMS: the Future of Memory and Storage 2024, the world's largest memory and storage industry conference, held in Santa Clara, CA.

The demonstration is straightforward. It compares the operation of a KIOXIA Enterprise SSD connected directly to a server via electrical cable to an optical SSD model connected by a 40 meter optical fiber cable. Although there is a significant difference in distance from the server at an actual data center, the demonstration showed that there was little difference in performance.
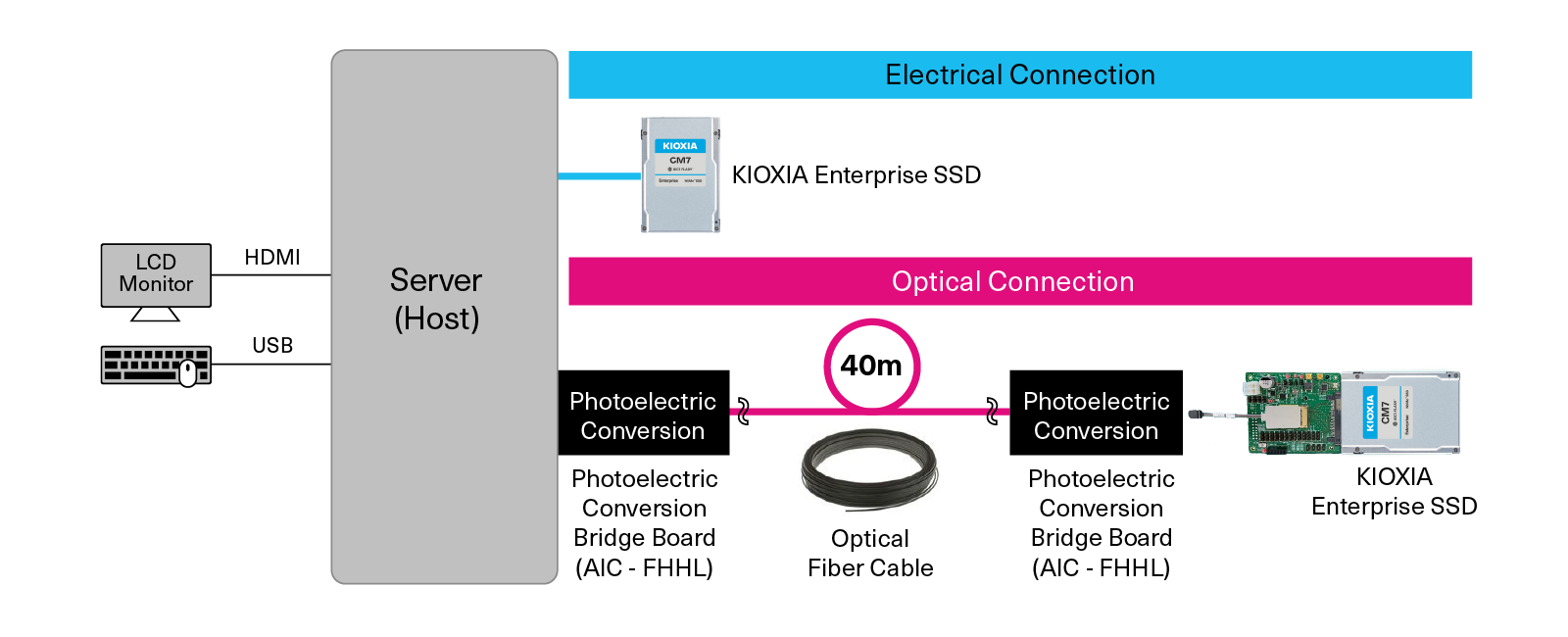
The Future of Optical SSDs
Optical SSDs from Kioxia have been presented and demonstrated in Europe, Taiwan, and Japan, with plans to exhibit at the Expo 2025 Osaka, Kansai, Japan. Valuable feedback has been received across various industries and regions on the development direction.
During the first half of the project, which focuses on research and development activities until March 2026, the plan is to gradually shift focus towards implementation, beginning after April 2026. To develop greener data centers, Kioxia will target systems and applications well suited for the expected use cases, and define specific market and customer segments. For example, by utilizing optical SSDs in a disaggregated system, a benefit will be sharing large volumes of data across multiple virtual systems without degrading performance. Kioxia will promote partnerships that enable the efficient operation of generative AI systems, enhancing everyday conveniences for our society.
- PCI Express, PCIe are registered trademarks of PCI-SIG.
- Other company names, product names, and service names may be trademarks of third-party companies.

